Margin Calls in Forex Trading – Main Talking Points:
- A short introduction to margin and leverage
- Causes of margin call
- Margin call procedure
- How to avoid margin calls
Margin and leverage
In the world of forex trading, margin and leverage play crucial roles in determining the profitability and risk associated with trades. Understanding these concepts is essential for any trader looking to navigate the intricacies of the market.
Margin:
Margin refers to the minimum amount of money required to place a leveraged trade. It acts as a form of collateral, allowing traders to gain exposure to larger positions without having to fund the full amount of the trade. In essence, it is the trader’s contribution to the overall trade.
Leverage:
Leverage, on the other hand, amplifies the exposure to the market. It is the ratio between the trader’s equity and the total position size. For example, a leverage of 1:100 means that for every $1 of equity, the trader can control $100 in the market.
It is important to note that while leverage can potentially lead to significant profits, it also comes with increased risk. Trading with leverage requires careful risk management to minimize potential losses.
What causes a margin call in forex trading?
A margin call occurs when a trader no longer has any usable or free margin in their trading account. This situation arises when trading losses reduce the usable margin below an acceptable level determined by the broker.
Margin calls are more likely to occur when traders commit a large portion of equity to used margin, leaving minimal room to absorb losses. From the broker’s perspective, implementing margin calls is a necessary mechanism to manage and reduce their risk effectively.
Below are the top causes for margin calls presented in no specific order:
- Holding onto a losing trade too long which depletes usable margin
- Over-leveraging your account combined with the first reason
- An underfunded account which will force you to overtrade with too little usable margin
- Trading without stops when price moves aggressively in the opposite direction
What happens when a margin call takes place?
When a margin call takes place, a trader’s positions are liquidated or closed out by the broker. This serves two main purposes: the trader no longer has sufficient funds in their account to hold the losing positions, and the broker becomes liable for the losses.
It is crucial to understand that leverage trading can result in situations where a trader owes the broker more than what has been initially deposited. This highlights the importance of responsible risk management and understanding the potential consequences of leverage.
To illustrate the process, let’s consider an example:
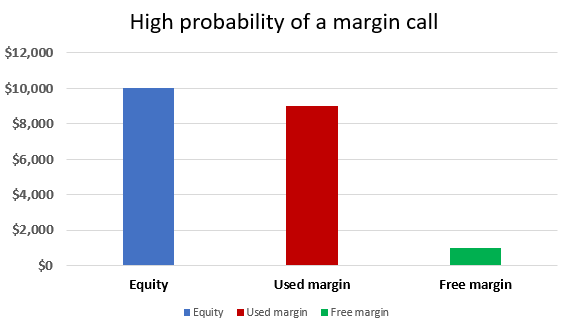
The trader has made a $10,000 deposit in their account and decides to trade four standard lots. With a margin percentage of 2% and the EUR/USD exchange rate at 1.125, the used margin is calculated as follows:

Trade size x price x margin percentage x number of lots
$100,000 x 1.125 x 0.02 x 4 lots = $9,000
In this scenario, the used margin of $9,000 represents a significant portion of the account equity, leaving a free margin of only $1,000. This indicates that the trader’s account is highly vulnerable to margin calls.
If the market moves more than 25 points against the trader, the margin call will be triggered. With each point worth $40, a movement of 25 points corresponds to $1,000, resulting in the liquidation of the position.
How to avoid margin call?
Leverage is often referred to as a double-edged sword, and for good reason. While it can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses. Therefore, implementing strategies to avoid margin calls is crucial for long-term trading success.
Here are four important ways to avoid margin calls in forex trading:
- Do not over-lever your trading account. It is recommended to use leverage in moderation, such as ten to one or even less.
- Exercise prudent risk management by implementing stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
- Maintain a healthy amount of free margin in the account to withstand market fluctuations. It is advisable to use no more than 1% of account equity on any single trade and no more than 5% equity on all trades collectively.
- Trade smaller sizes and approach each trade as one of many insignificant trades. This mindset helps to avoid overexposure and reduce the impact of potential losses.
By following these strategies, traders can significantly reduce the likelihood of margin calls and preserve their trading capital more effectively.
Free resources to enhance your trading
Continuous learning and improving trading skills are essential for success in the forex market. Here are some free resources that can enhance your trading journey:
- If you are new to forex trading, our free New to Forex guide provides a comprehensive introduction to the basics.
- Explore our range of trading guides that cover various aspects of forex trading, helping you develop effective strategies and expand your knowledge.
- Understanding margin and leverage is critical for managing risk. Familiarize yourself with these concepts to make informed trading decisions.
- Our research team has analyzed over 30 million live trades to uncover the Traits of Successful Traders. Incorporate these traits into your trading approach to gain an edge in the markets.
Remember, forex trading requires continuous education, disciplined risk management, and a well-thought-out trading plan. By utilizing the available resources and implementing sound trading strategies, traders can increase their chances of success and mitigate the risk of margin calls.
